Looking for an online encyclopedia about cricket ground all fielding positions? You are in the right place. In this article, we have explained every aspect of the cricket ground and positions in a simple and easy way. You will also find a clear visual representation of cricket fielding positions. This guide is ideal for beginners and anyone looking to improve their knowledge of cricket. Read on.
Table of Contents
Cricket Ground Positions Name—Complete List
Here is the complete list of all the general fielding positions in cricket ground:
|
Fielding Position |
Side of Batter | Typical Distance from Batter |
|
Bowler |
Center |
20.12 m (pitch length) |
|
Wicketkeeper |
Behind batter |
2–3 m |
|
Slip |
Off side |
10–15 m |
|
Fly Slip |
Off side |
20–30 m |
|
Gully |
Off side |
15–25 m |
|
Point |
Off side |
25–35 m |
|
Backward Point |
Off side | 30–45 m |
| Cover | Off side |
25–35 m |
|
Extra Cover |
Off side |
30–40 m |
|
Mid-Off |
Off side | 15–25 m |
| Long Off | Off side (deep) |
65–75 m |
|
Deep Cover |
Off side (deep) |
65–75 m |
|
Deep Extra Cover |
Off side (deep) | 65–75 m |
| Third Man | Off side (behind) |
30–50 m |
|
Deep Third Man |
Off side (deep) | 65–75 m |
| Square Leg |
Leg side |
20–40 m |
|
Backward Square Leg |
Leg side |
30–50 m |
|
Fine Leg |
Leg side (behind) | 30–60 m |
| Deep Fine Leg | Leg side (deep) |
65–75 m |
|
Long Leg |
Leg side (deep) |
65–75 m |
|
Midwicket |
Leg side | 25–40 m |
| Deep Midwicket | Leg side (deep) |
65–75 m |
|
Short Leg |
Leg side (close) | 5–10 m |
| Leg Slip | Leg side (behind) |
10–15 m |
|
Leg Gully |
Leg side | 15–20 m |
| Silly Point | Off side (close) |
5–10 m |
|
Mid-On |
Leg side | 15–25 m |
| Long On | Leg side (deep) |
65–75 m |
|
Deep Point |
Off side (deep) | 65–75 m |
| Deep Square Leg | Leg side (deep) |
65–75 m |
Did You Know? In modern-day cricket, captains of the fielding team do not always use fixed fielding positions. Depending on the situation of the game, they place their fielders in other positions that do not have fixed names. These are simply small changes or modifications of the existing positions.
A fielder may move a few steps to the left or right. Sometimes, the fielder stands a little closer to the batter. Other times, the fielder moves deeper toward the boundary.
Cricket Ground All Positions—Leg Side of the Batter
Let us quickly understand all the positions of fielders in cricket ground which is to the leg side of a batsman.
Square Leg
The square leg is one of the most common cricket ground fielding positions. It is located on the leg side. The fielder stands at roughly 90 degrees (square) to the batter. The distance can be 20 to 40 meters from the batter. It can vary depending on the match format. The fielder in this position is placed to stop shots played off the pads and catch balls flicked in the air.
Fine Leg
A Fine leg fielder stands behind the batter on the leg side. The player stands close to the wicketkeeper’s line. The distance is usually 30 to 60 meters. This fielder is positioned to stop edges, glances, and deflections that go very fine past the batter.
Long Leg
Long leg is one of the cricket ground field positions that is near the boundary line. Here, the fielder stands deep on the leg side. The distance is usually 65 to 75 meters from the pitch. This fielder mainly saves boundaries and catches high shots played behind the batter.
Deep Fine Leg
The deep fine leg is similar to the fine leg but placed closer to the boundary. This position is used when batters are likely to play scoop or flick shots. The fielder’s main job is to catch aerial shots and save four or six runs. This is one of those ground positions in cricket that is popular in the limited format of the game.
Mid Wicket
Midwicket is located on the leg side between mid on and square leg. The distance is usually 25 to 40 meters. This fielder is placed to stop pull shots, flicks, and on side drives.
Deep Mid Wicket
The deep midwicket position is near the boundary on the leg side. The distance is around 65 to 75 meters away (can vary from one ground to the other). This position is used against batters who are more likely to play big shots. It is one of the most common fielding positions of cricket ground, especially when a spinner is bowling.
Short Leg
Short leg stands very close to the batter, usually 5 to 10 meters away. You will often see this fielding position in Test format. This fielder wears a helmet and pads for safety. The role is to catch bat-pad chances and quick defensive shots.
Leg Slip
Leg slip stands behind the batter, near the wicketkeeper, on the leg side. Again, this position is mostly used in Test matches. The fielder stands in this position looking to catch fine edges from leg-side defensive shots.
Leg Gully
Leg gully stands between leg slip and square leg. The distance is around 15 to 20 meters away. This is one of the most rarely used field positions in cricket ground. Mostly, when a fast bowler is bowling, the captain sets a fielder in this position so that he or she can take advantage of sharp edges and take quick catches.
Backward Square Leg
The backward square leg stands behind the square on the leg side. The distance is around 30–50 meters. This fielder is positioned to stop late glances. It is a great, “quick single-saver” option for the fielding team.
Cricket Positions in Ground—Off Side of the Batter
The following are the cricket ground different positions located on the right side of a batsman:
Slip
Slip stands next to the wicketkeeper on the off side. The distance is usually 10 to 15 meters from the batter. This position is mainly used when a fast bowler is bowling. The fielder is placed here to catch sharp edges that come off the bat.
Fly Slip
The fly slip stands deeper than a normal slip position. The distance is around 20 to 30 meters. This fielder is placed when edges are likely to carry in the air. The main role is to catch high edges from the batter.
Gully
Gully stands between slip and point on the off side. The distance is usually 15 to 25 meters. This fielder is placed to catch hard edges off the bat. It is a common position in Test and first-class cricket.
Point
A point fielder stands square on the offside of the batter. The distance is around 25 to 35 meters. This fielder stops cut shots and square drives. Quick reflexes are very important in this position.
Backward Point
A Backward point fielder stands behind the point on the offside. The distance is usually 30 to 45 meters. This position is mainly used to save runs. The fielder stops late cuts and guided shots.
Cover
The Cover fielder stands in front of the point on the offside. The distance is around 25 to 35 meters. This fielder is placed to stop strong ground shots. Cover is an important position for saving quick runs.
Extra Cover
Extra cover stands wider than the cover position. The distance is usually 30 to 40 meters. This fielder stops powerful offside drives. Extra cover is very important in limited overs cricket.
Mid Off
Mid off stands close to the bowler on the off side. The distance is around 15 to 25 meters. This fielder stops straight drives. Mid-off also helps in stopping quick singles.
Long Off
Long off stands deep on the off side, near the boundary. The distance is usually 65 to 75 meters. This fielder is placed to catch lofted shots. Long off fielder also helps in saving boundaries.
Deep Cover
Deep cover stands near the boundary on the offside. This position is used when batters play aerial cover drives. The main role of this fielder is to stop fours and sixes.
Deep Extra Cover
Deep extra cover stands wider near the boundary. This fielder is placed for very powerful off-side shots. Good catching and boundary-saving skills are needed here.
Third Man
The third man stands behind the batter on the off side. The distance is usually 30 to 50 meters. This fielder stops edges and guided shots. The third man is also used to save easy runs.
Deep Third Man
Deep third man stands close to the boundary behind the batter. This position is common in T20 and ODI cricket. The fielder saves boundaries and catches top edges.
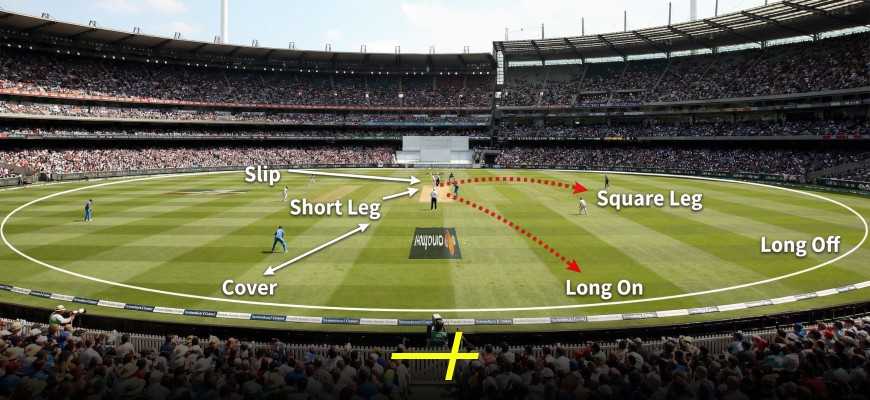
Cricket Ground Positions Chart—Graphical View
Up until this point, we have shared all the usual cricket ground positions names. To make things even clearer and easier to understand, we’ve created a detailed visual guide. You can check the cricket ground images with fielding positions below:
Now that you know all the cricket match ground positions, you have upgraded your cricketing wisdom. Do not let it go to waste. Join us on Parimatch and predict the outcome of cricket matches. Bet on IPL, BBL, CPL, ICC, and more and win. To start cricket betting, create your free account today. Download our app and join the action with your fingertips.
FAQs:
What are the most common cricket fielding positions?
Slip, gully, point, cover, mid-off, mid-on, square leg, fine leg, long-on, and long-off are the most common fielding positions in cricket ground.
What are the ICC rules for cricket fielding?
According to the ICC rules for cricket fielding, the captain of the bowling side can place no more than five fielders outside the 30 yard circle.
How is the point and mid off different?
A point fielder is placed on the off side, square of the batter. On the other hand, a Mid off fielder stands straighter and closer to the bowler
Can fielding positions change during an over?
Yes, fielding positions can change during an over. However, after a no-ball, if the same batter remains on strike, the captain cannot change the field during the free hit.